Big Data Platforms
DSBA-6190 Discussion: Week 11
A note on the series:
This post is part of a series of weekly discussion prompts for my class DSBA-6190: Introduction to Cloud Computing. Each prompt includes two or three general questions on a cloud computing related topic, along with screenshot from a interactive online lab.
What problems does Hadoop solve?
With the amount of available data in the world continuing to grow, tools that are capable of handling this of data are needed. Hadoop is one of those tools. It’s initial release was in 2006, and at that time if you were a company that wanted to really take-on this growing amount of data, you probably had to invest in a very large, high performing, expensive system. On top of that, there was a good chance your system would be out-paced by the data before you knew it.
What made Hadoop extremely useful and effective is that it didn’t rely on larger and more powerful state-of-the-art hardware. Instead, it took the opposite approach. Hadoop allows for distributed processing, meaning and single process is distributed across a set of machines. So, in theory, if you had a process that was bogging down your machine, you could use Hadoop to split it to a second machine, dividing the burden. Or even better, you could split it across thousands of machines! This would allow you to process extremely large amounts of data. Even better, the machines Hadoop is using can be standard, off-the-shelf machines. Machines that are prone to failure, but with Hadoops distributed system, that failure can be detected and overcome, maintaining a high-availability service.
There are few different problems Hadoop is useful for, and they are all Big Data problems.
- Data Processing: Performing database-like processing on massive amounts of data (think tera- or petabyte level). Anything smaller and you don’t get the savings with Hadoop. There are better options.
- Data Storage: Storing diverse sets and types of data, structured or unstructured. Hadoop does not require a Schema.
- Parallel Processing: MapReduce allows these petabytes of data to be split into smaller, manageable chunks, each processed in parallel. MapReduce then re-aggregates the dispersed analysis to yield a consolidated output.
Resources
Thank you to the following resources for help and input on this question.
- https://www.hostingadvice.com/how-to/what-is-hadoop/
- https://www.dezyre.com/article/hadoop-explained-how-does-hadoop-work-and-how-to-use-it-/237
- https://hadoop.apache.org/
What are the key differences between Hadoop and Spark?
While the question asks about the differences between Hadoop and Spark, these services are different enough that comparison is difficult. It is much more straight forward to compare Spark to MapReduce, as they are both data processing methods using a distributed system.
Similar to Hadoop and MapReduce, Spark works as a distributed system, working across many machines. The key effective difference is Spark reads data and performs computations in-memory. This helps increase the possible processing speeds by up to 100x. The same increases speed can be very useful for training machine learning models. Spark has its own machine learning library (MLib) that make it possible to train these models to the same large-scale, real time date.
So, where would you use Spark? I’ve already gone over some use-cases with Hadoop in the previous question. What Spark excels at is real-time analysis. Spark’s faster processing times allow it to process data streams in nearly real-time, while still dealing with the extremely large-scale sizes of data that Hadoop is also used for.
While there are key differences between the two systems, it is not an either/or situation. Both systems have their strengths and weaknesses which make them the right tool for different jobs. In fact, when correctly use, these different powerful systems complement each other.
Resources
Thank you to the following resources for help and input on this question.
- https://www.datamation.com/data-center/hadoop-vs.-spark-the-new-age-of-big-data.html
- https://intellipaat.com/blog/what-is-apache-spark/
- https://spark.apache.org/
Interactive Lab
Post a screenshot of a lab where you had difficulty with a concept or learned something.
This week I completed Lab 1 - Introduction to AWS IAM of the Academy Cloud Foundations v2 class on Vocareum. This lab explored Amazon Web Services IAM service.
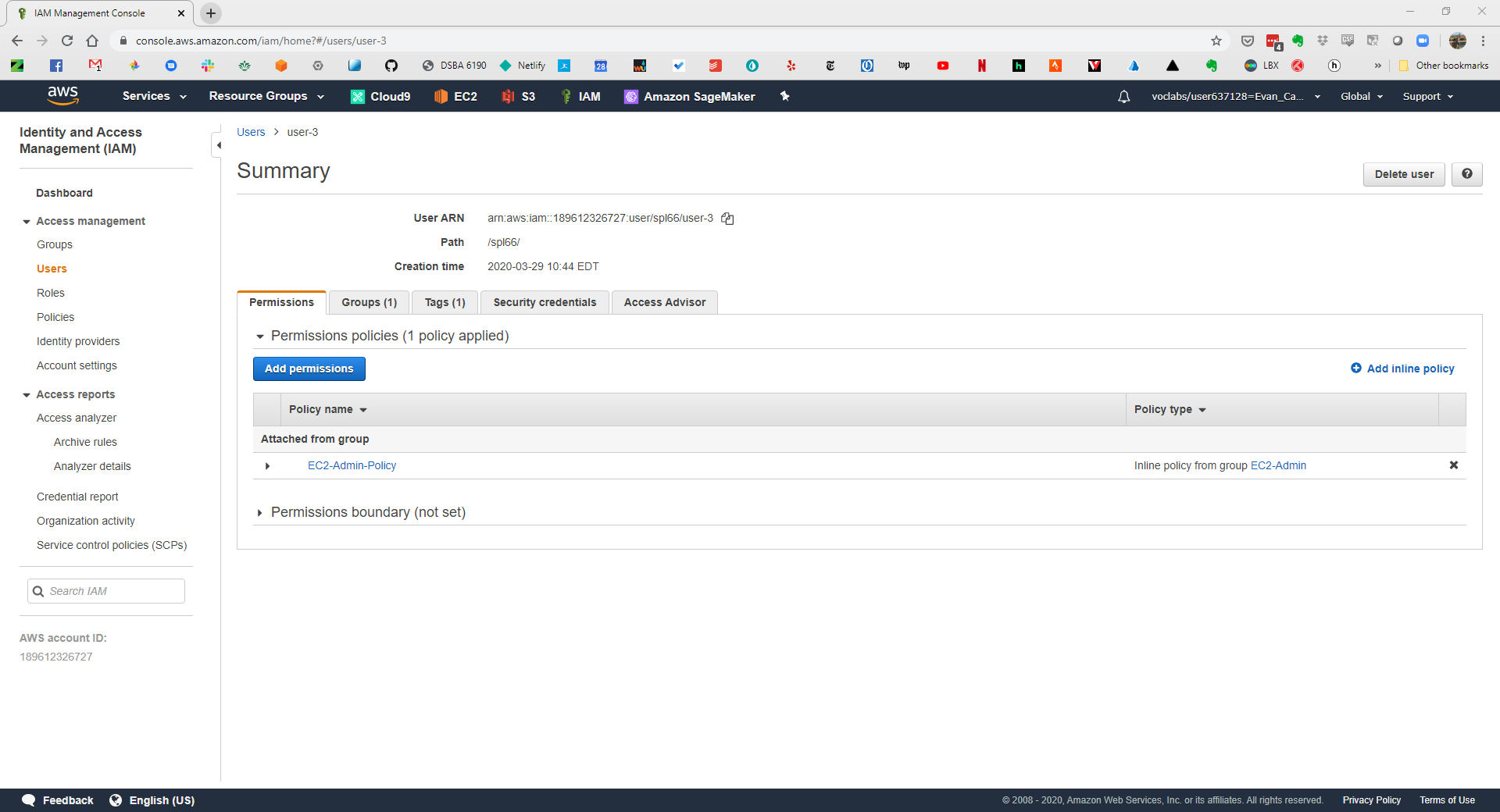
This was a pretty straighforward look at applying policies to users in IAM. The Group function makes applying the same permissions to multiple people very easy. I was also very interested in user-3 in the lab. This user did not get a Managed Policy. Instead, an Inline Policy was applied. These are useful for one-off situations.