Machine Learning on the Edge
DSBA-6190 Discussion: Week 13
A note on the series:
This post is part of a series of weekly discussion prompts for my class DSBA-6190: Introduction to Cloud Computing. Each prompt includes two or three general questions on a cloud computing related topic, along with screenshot from a interactive online lab.
What problems does edge-based machine learning solve?
To understand the problems edge-based machine learning might solve, we need to define edge-based computing. In the last few years this concept has become a buzzword, like “Big Data”, but with different meanings for different people. For this discussion, the edge in “edge-computing” is used in a geographic sense. As opposed to cloud-based computing, where computing is done on a cloud server, edge-based computing happens at the source of the data.
So, why then would someone want to move machine learning functions from cloud servers to edge devices? One of the big reasons is time. Let’s say you have an image that you took on a local device, like a cell phone, and you want to perform an inference on that image. If the machine learning model is hosted on a cloud server, that image needs to be transmitted from your phone, to the cloud server, with the inference result returning to your phone. That’s a very simplified pipeline, omitting numerous steps for image conversion to different formats for it to make that journey. When the inference takes place on your local device, you lose that latency. So long as the device has the computational power, the inference is returned much faster.
A clear extension of the latency issue is what if you need to make a machine learning inference and you don’t have connection to the cloud at all? In those cases, you need the machine learning framework to be local. Consider the Resource Extraction industries (mining, oil & gas, etc.). These industries often operate in areas where connectivity is not guaranteed. If the machine learning framework is included with the edge-devices in these locations, such as instrument sensors, then the machines can still use machine learning inferences in their work.
Resources
Thank you to the following resources for help and input on this question.
- What is edge computing?
- Why Machine Learning on The Edge?
- [](https://towardsdatascience.com/edge-ai-cc478f9fbb5a) Why and how to run machine learning algorithms on edge devices
What are the machine learning frameworks most widely used with edge inference?
Three of the biggest players in developing edge machine learning systems are Google, Facebook, and Apple.
Apple
For Apple, Core ML 3 is their primary machine learning framework. They also have ARKit 3 for augmented reality tasks.
For Google, Tensorflow is the base of their machine learning framework. But the TensorFlow environment has grown to include TensorFlow Lite. TensorFlow Lite provides a stripped down framework better suited for mobile machine learning tasks. In addition, Google has the Edge TPU chip, an edge-computing variant of the Cloud TPU chip.
For Facebook, Pytorch is the base of their machine learning framework. The recent release of Pytorch 1.3 included experimental support for mobile features.
Resources
Thank you to the following resources for help and input on this question.
Interactive Lab
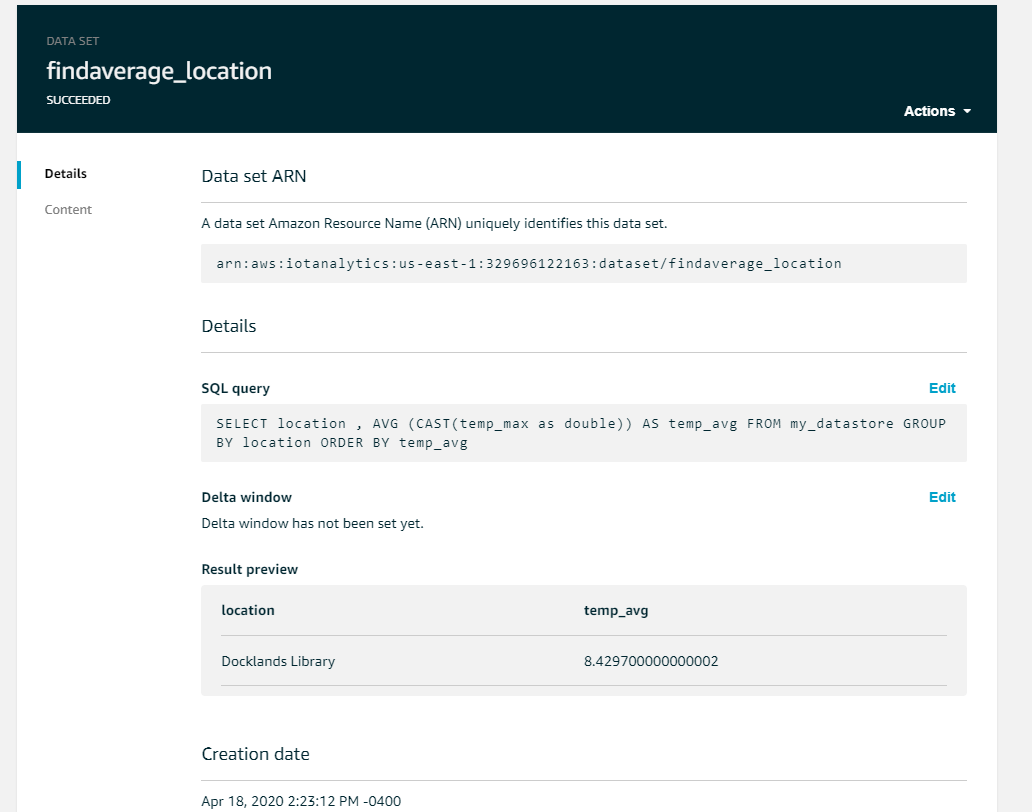
Post a screenshot of a lab where you had difficulty with a concept or learned something.
This week the training was Analyze Iot Data with AWS IoT Analytics from Vocareum Academy Data Analytics. This training interacted with Amazon Web Services Internet of Things services. Setting up a pipeline was a little more complex than I expected, but once it was set up, it was really easy to extract information with some basic SQL calls.